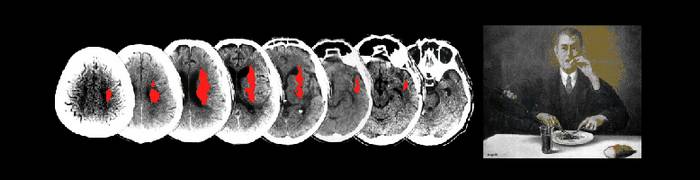
Ten patients with idiopathic dystonia and twelve healthy controls were tested with pairs of non-noxious electrical stimuli separated by different time intervals. Stimuli were delivered (i) to the pad of the index finger (same-point condition), (ii) to the pad and to the base of the index finger (same-finger condition) and (iii) to the pad of the index and ring fingers (different-fingers condition). Subjects were asked to report if they perceived single or double stimuli in the first condition and synchronous or asynchronous stimuli in the second and third conditions. STDTs were significantly higher in dystonic than control subjects in all three conditions. Results extend current knowledge on deficits of somesthetic temporal discrimination in dystonia by showing that temporal deficits are not influenced by spatial variables.

Neurol Sci. 2002 Sep;23 Suppl 2:S113-4