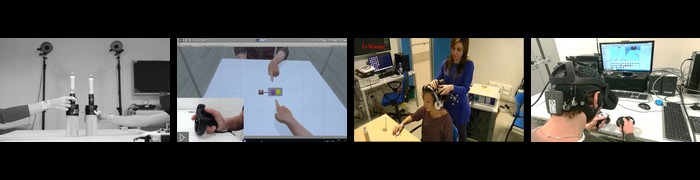
Peripersonal Space (PPS) is defined as the space close to the body where all interactions between the individual and the environment take place. Behavioural experiments on PPS exploit multisensory integration, using Multisensory Visuo-Tactile stimuli (MVT), whose visual and tactile components target the same body part (i.e. the face, the hand, the foot). However, the effects of visual and tactile stimuli targeting different body parts on PPS representation are unknown, and the relationship with the RTs for Tactile-Only stimuli is unclear. In this study, we addressed two research questions: (1) if the MVT-RTs are independent of Tactile-Only-RTs and if the latter is influenced by time-dependency effects, and (2) if PPS estimations derived from MVT-RTs depend on the location of the Visual or Tactile component of MVTs. We studied 40 right-handed participants, manipulating the body location (right hand, cheek or foot) and the distance of administration. Visual and Tactile components targeted different or the same body parts and were delivered respectively at five distances. RTs to Tactile-Only trials showed a non-monotonic trend, depending on the delay of stimulus administration. Moreover, RTs to Multisensory Visuo-Tactile trials were found to be dependent on the Distance and location of the Visual component of the stimulus. In conclusion, our results show that Tactile-Only RTs should be removed from Visuo-Tactile RTs and that the Visual and Tactile components of Visuo-Tactile stimuli do not necessarily have to target the same body part. These results have a relevant impact on the study of PPS representations, providing new important methodological information.

Exp Brain Res. 2022 Apr;240(4):1205-1217. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06324-8