BACKGROUND: Studies in healthy people show that stimulation of muscle spindles through frequency-specific tendon vibration (TV) induces the illusory perception of movement. Following spinal cord injury (SCI), motor and sensory connections between the brain and parts of the body below-the-lesion level are partially or totally impaired.
OBJECTIVE: The present investigation is a descriptive study aimed to investigate whether people living with SCI may experience movement illusions comparable to a control group.
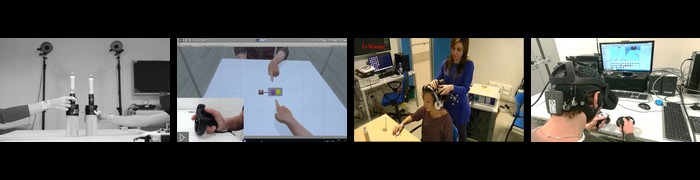
METHODS: Healthy and people with SCI were asked to report on three illusion-related features (Vividness, Duration, Illusory Extension) after receiving 70 Hz TV on the biceps brachii tendon of both arms. Two different forces of stimulation were applied: 2.4 N and 4.2 N.
RESULTS: Both patients and controls were susceptible to the kinesthetic illusion. However patients presented lower sensitivity to TV than healthy subjects. Participants rated stronger illusions of movement after 4.2 N than 2.4 N stimulation in all the three illusion-related features. Further, patients reported atypical illusory experiences of movement (e.g. as if the arm wanted to extend, or a sensation of pushing against something) that may reflect different reorganization processes following spinal cord injury.
CONCLUSION: The study provides a preliminary evidence of the possible use of the proprioceptive stimulation in the upper limbs of people living with SCI. Results are discussed in the light of recent advancements of brain-computer applications based on motor imagery for the control of neuroprosthetic and robotic devices in patients with severe sensorimotor deficits.

Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2016 Aug 19. doi: 10.3233/RNN-160660. [Epub ahead of print]