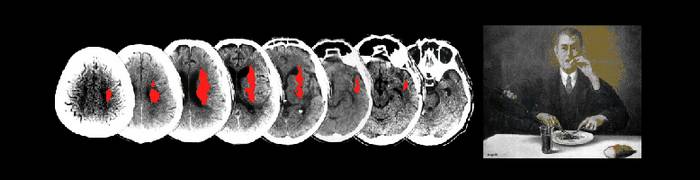
The illusory subjective experience of looking at one's own face while in fact looking at another person's face can surprisingly be induced by simple synchronized visuotactile stimulation of the two faces. A recent study (Apps MA, Tajadura-Jiménez A, Sereno M, Blanke O, Tsakiris M. Cereb Cortex. First published August 20, 2013; doi:10.1093/cercor/bht199) investigated for the first time the role of visual unimodal and temporoparietal multimodal brain areas in the enfacement illusion and suggested a model in which multisensory mechanisms are crucial to construct and update self-face representation.

J Neurophysiol. 2015 Apr 1;113(7):1959-62. doi: 10.1152/jn.00872.2013. Epub 2014 Jul 2.