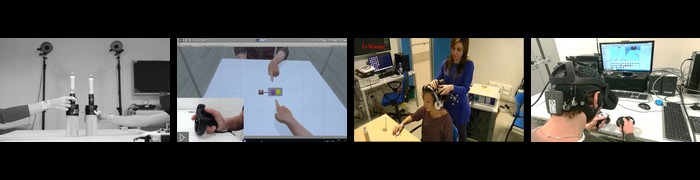
During social interactions people automatically apply stereotypes in order to rapidly categorize others. Racial differences are among the most powerful cues that drive these categorizations and modulate our emotional and cognitive reactivity to others. We investigated whether implicit racial bias may also shape hand kinematics during the execution of realistic joint actions with virtual in- and out-group partners. Caucasian participants were required to perform synchronous imitative or complementary reach-to-grasp movements with avatars that had different skin color (white and black) but showed identical action kinematics. Results demonstrate that stronger visuo-motor interference (indexed here as hand kinematics differences between complementary and imitative actions) emerged: i) when participants were required to predict the partner's action goal in order to on-line adapt their own movements accordingly; ii) during interactions with the in-group partner, indicating the partner's racial membership modulates interactive behaviors. Importantly, the in-group/out-group effect positively correlated with the implicit racial bias of each participant. Thus visuo-motor interference during joint action, likely reflecting predictive embodied simulation of the partner's movements, is affected by cultural inter-individual differences.

Sci Rep. 2015 Feb 17;5:8507. doi: 10.1038/srep08507