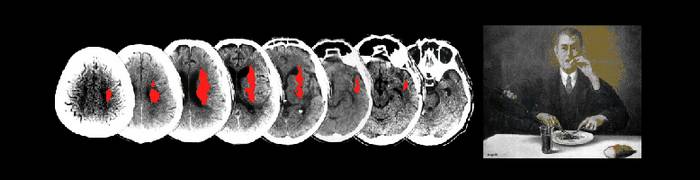
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)

Functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI, is a technique for measuring brain activity. The procedure is similar to MRI but uses the change in magnetization between oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood as its basic measure. It works by detecting changes in blood oxygenation and flow that occur in response to neural activity. When a brain area is more active it consumes more oxygen and, to meet this increased demand, blood flow increases to the active area. fMRI is becoming the diagnostic method of choice for learning how a normal, diseased or injured brain is working. Since the early 1990s, fMRI has…
Electroencephalography (EEG)

EEG is a non-invasive tool for the direct recording of electrical signatures of neural activity via electrodes positioned over the scalp, that has the unique advantage of recording very high time-resolution data, in the order of milliseconds. A state-of-the art EEG/ERP facility is available at the lab. This facility houses two 32 channels Snyamps amplifiers, a Laser Neurolabs YAP Elen, E-Prime software for the presentation of experimental stimuli, and Brain Vision Analyzer, EEGLAB and BESA softwares for EEG/ERPs data analyses. By means of Event-related potentials (ERPs) is possible to measure brain activity just before, during, and after an event of…
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) and Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS)

Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is delivered to the brain by passing a strong brief electrical current through an insulated wire coil placed on the skull. This rapid phasic current flow generates a transient magnetic field, which propagates in space and in turn induces a secondary current in the brain that is capable of depolarising neurons if the coil is held over the subject’s head (Pascual-Leone et al., 2002). Single-pulse TMS of the primary motor cortex (M1) allows recording the amplitude of Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP). MEP amplitude is a measure of the cortico-spinal reactivity and is known to reflect the…
Thermal Imaging (TII)
Thermal Imaging (TII) is a very-sensitive, state-of-the-art contact-free methodology able to estimate variations in autonomic activity. Such variations are reflected in changes of cutaneous temperature that can be detected by recording the thermal infrared signals spontaneously released by the human body. TII has been previously used to detect deception showing a high accuracy. Being completely non invasive, the TI is particularly indicated for developmental research. In this study we will perform Thermal TII imaging by means of a digital thermal camera (FLIR SC3000, FlirSystems, Sweden), with a Focal Plane Array of 320 x 240 QWIP detectors, capable of collecting the…
Laser Evoked Potentials (LEP)

The study of any sensory system requires the availability of a quantifiable stimulus that activates selectively the sensory system under investigation. Until recently, in contrast with other sensory systems (e.g., auditory, visual), specific nociceptive stimulators had not been available. Transcutaneous electrical stimuli are easy to control, and activate the peripheral afferents in a highly synchronous manner. However, the large diameter of Aβ non-nociceptive afferents results in an activation threshold that is lower than that of Aδ and C nociceptive afferents. Thus, when the intensity of electrical stimulation is above the threshold of nociceptive afferents, the coactivation of mechanoreceptors is unavoidable.…
Immersive Virtual Reality (IVR)

An immersive virtual environment (IVR) is a computer-generated surrounding projected on (stereoscopic) display. Observer’s viewpoint is tracked and imges are updated in real-time. This delivers a life-sized virtual reality within which a person can experience events and interact with representations of virtual objects or humans. Experiments take place in ”Cave” with three back-projected vertical screens (3 m×2.2 m) and a floor screen (from a ceiling mounted projector) (3 m×3 m). Previous works showed that people tend to respond realistically to virtual humans and to events within such environments. For example, IVR has been used in studies of social anxiety and…
Kinematics
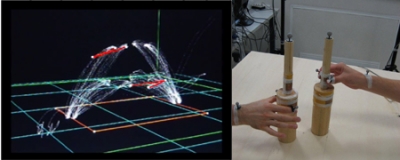
Movement kinematics will be recorded by using an ELITE motion analysis system (Bioengineering Technology & Systems [B|T|S]). The ELITE system has been designed for automatic and reliable analysis of body movements based on real-time processing of TV images. The fast processor for shape recognition (FPSR) constitutes the core of the ELITE system. It processes the TV image provided by several simultaneously recording infrared cameras and it uses a dedicated algorithm to: i) recognize markers only if their shape matches a determined mask, ii) compute markers coordinates in 2D space; information are then stored in order to off-line perform cross-correlations between…
Physiological measures
Our Powerlab 8/30 (ADInstruments; Model ML870), an 8-input channel high-performance data acquisition system, allows the recording of several measures such as: bioloelectrical potential signals (e.g. electrocardiography and electromyography); galvanic responses (GSR Amp ML116) pulse rate (Pulse transducer MP100); and respiratory signals (Respiratory Belt Transducer MLT1132). The possibility to simultaneously record several physiological measures allows the dissection of various axis of bodily responses related to emotional experience. Furthermore, combining autonomic measures with other relevant techniques that measure brain activity, such as such event related potentials and functional magnetic resonance, provides an empirical basis for understanding brain functioning and brain-body interaction.
Eye Tracking
Eye movements may provide an important information on the cognitive processing of a visual scene, while the pupil size, which reflects the activity of the orto-sympathetic autonomic system, may provide an important info on the affective processes at play. Furthermore, our Applied System lab (ASL) 504 eye-tracking camera can sample eye movements up to 240Hz, which allowed us to collect fine-grained RTs and accuracy information.
Phasic EMG
Facial activity will be recorded with bipolar MRI-compatible electrodes attached over the zygomaticus major (involved in happy facial expressions) and corrugator supercilii (involved in fearful and anger expressions). EMG signal will be recorded at a sampling rate of 1024 Hz and band-pass filtered (20-500 Hz). Comparison between different stimulus conditions will be computed for mean peak of activities as well as at each time point to reveal the amplitude and temporal profile of the EMG response.4. Innovative research tools. In addition to the state-of-the-art but already established methodologies described above, we will use two emerging research tools that are particularly…